Understanding Psoriatic Arthritis: Key Signs That Indicate a Potential Problem
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects countless individuals around the world. Despite its link to psoriasis, this form of arthritis can impact more than just the skin—it can also lead to painful, swollen joints and long-term joint damage if left untreated. Psoriatic arthritis occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, causing inflammation in both the skin and joints. Recognizing the early signs of psoriatic arthritis is essential for timely diagnosis and effective management. A clear understanding of these symptoms can help prevent complications and support long-term health and mobility.
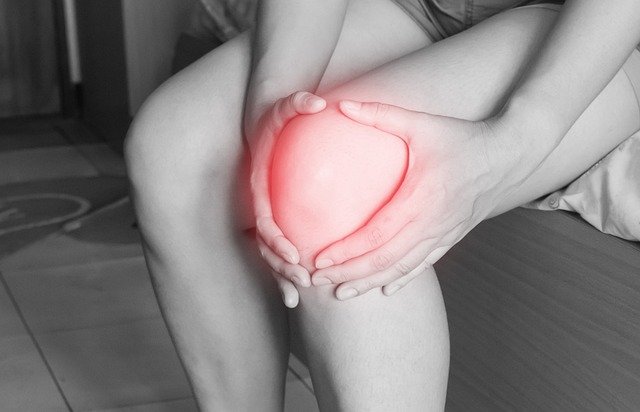
What is joint pain and how does it relate to psoriatic arthritis?
Joint pain is a hallmark symptom of psoriatic arthritis and often serves as one of the first indicators of the condition. In psoriatic arthritis, inflammation caused by the immune system’s attack on healthy tissue leads to pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints. This pain can range from mild to severe and may affect various joints throughout the body, including the fingers, toes, wrists, ankles, and lower back. Unlike some other forms of arthritis, psoriatic arthritis can affect joints on one or both sides of the body asymmetrically. The pain may be accompanied by warmth and tenderness in the affected areas, making everyday activities challenging.
How does fatigue and lethargy manifest in psoriatic arthritis patients?
Fatigue and lethargy are common yet often overlooked symptoms of psoriatic arthritis. The chronic inflammation associated with the condition can lead to persistent tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest. Many patients describe this fatigue as an overwhelming sense of exhaustion that affects both physical and mental functioning. It can interfere with daily activities, work performance, and overall quality of life. The fatigue experienced in psoriatic arthritis is thought to be a result of the body’s ongoing immune response and the energy expended in fighting inflammation. Additionally, the pain and discomfort associated with the condition can disrupt sleep patterns, further exacerbating feelings of tiredness and lethargy.
Why is monitoring swelling in joints important for psoriatic arthritis?
Monitoring joint swelling is crucial in the management of psoriatic arthritis as it provides valuable information about disease activity and progression. Swelling occurs when inflammation in the joints causes an increase in synovial fluid and thickening of the joint lining. This can lead to visible puffiness, warmth, and reduced range of motion in the affected areas. Regular assessment of joint swelling helps healthcare providers gauge the effectiveness of treatment plans and make necessary adjustments. Furthermore, persistent swelling can contribute to long-term joint damage if left unchecked. By closely monitoring swelling, patients and their healthcare teams can work together to minimize inflammation, prevent joint destruction, and maintain optimal function.
How can recognizing nail or skin changes help in identifying psoriatic arthritis?
Nail and skin changes are distinctive features that can aid in the early identification of psoriatic arthritis. Up to 90% of people with psoriatic arthritis also have psoriasis, a condition characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin. These skin lesions often appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. In some cases, psoriatic arthritis can develop before skin symptoms become apparent. Nail changes are also common and can include pitting, ridging, thickening, and separation from the nail bed (onycholysis). These nail alterations may occur in up to 80% of psoriatic arthritis patients and can be an early indicator of the condition. Recognizing these skin and nail changes can prompt earlier medical evaluation and diagnosis, leading to timely treatment and better long-term outcomes.
What role do weight and lifestyle changes play in psoriatic arthritis management?
Weight management and lifestyle modifications play a significant role in the overall treatment approach for psoriatic arthritis. Excess weight puts additional stress on joints, particularly weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips, potentially exacerbating pain and inflammation. Studies have shown that losing weight can reduce disease activity and improve treatment response in overweight or obese patients with psoriatic arthritis. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through proper nutrition and regular exercise can help manage inflammation, improve joint function, and enhance overall well-being.
In the United States, where obesity rates are high, addressing weight management is particularly crucial for psoriatic arthritis patients. A Mediterranean-style diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, has been associated with reduced inflammation and improved symptoms in some studies. Regular physical activity, tailored to individual capabilities, can help maintain joint flexibility, strengthen muscles, and improve cardiovascular health. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, or yoga are often recommended for their joint-friendly nature.
How can early detection and treatment improve psoriatic arthritis outcomes?
Early detection and prompt treatment of psoriatic arthritis are critical for preventing joint damage and maintaining quality of life. The progressive nature of the disease means that without appropriate intervention, joint destruction can occur, leading to permanent disability. Recognizing the key signs and symptoms discussed earlier allows for timely medical evaluation and diagnosis. Once diagnosed, a variety of treatment options are available, ranging from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for mild cases to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic therapies for more severe manifestations.
| Treatment Type | Provider Type | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs | Primary Care Physician | Pain relief, reduced inflammation |
| DMARDs | Rheumatologist | Slows disease progression, joint protection |
| Biologic Therapies | Rheumatologist | Targets specific immune pathways, effective for severe cases |
| Physical Therapy | Licensed Physical Therapist | Improves joint function, strengthens muscles |
| Occupational Therapy | Licensed Occupational Therapist | Enhances daily living skills, joint protection techniques |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Early intervention with appropriate treatments can significantly improve long-term outcomes, reducing joint damage, preserving function, and enhancing overall quality of life for individuals with psoriatic arthritis. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications all contribute to better management of this chronic condition.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




