Breathing Patterns That Disrupt Your Sleep
Many people experience restless nights without realizing that their breathing patterns may be the underlying cause. Irregular breathing during sleep can lead to frequent awakenings, reduced oxygen levels, and poor sleep quality. Understanding how nighttime breathing issues affect your rest is essential for identifying potential problems and finding effective solutions to improve your overall sleep experience and daytime alertness.
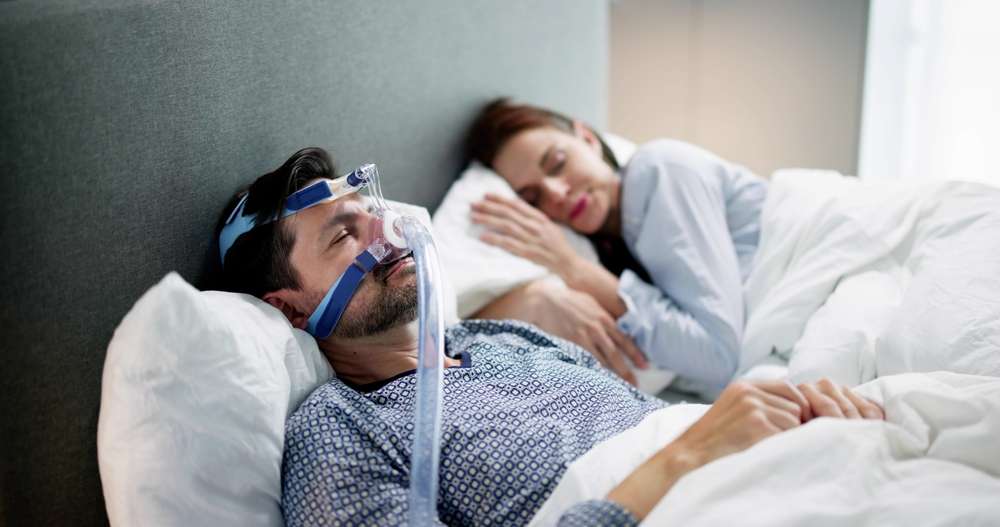
Disrupted breathing during sleep affects millions of individuals and can significantly impact overall health and well-being. When breathing becomes irregular, shallow, or temporarily stops during the night, the body’s natural sleep cycle is interrupted, leading to fragmented rest and daytime fatigue. Recognizing the signs and understanding the mechanisms behind these breathing disruptions can help you take appropriate steps toward better sleep and improved quality of life.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
What Causes Nighttime Breathing Issues?
Several factors contribute to irregular breathing patterns during sleep. Anatomical features such as a narrow airway, enlarged tonsils, or a thick neck circumference can restrict airflow. Excess weight, particularly around the neck and throat area, can put pressure on the airway and cause it to collapse during sleep. Age also plays a role, as muscle tone in the throat naturally decreases over time, making airways more susceptible to obstruction. Additionally, sleeping position, alcohol consumption before bed, and certain medications can relax throat muscles excessively, leading to breathing difficulties.
Chronic nasal congestion, whether from allergies, sinus problems, or structural abnormalities like a deviated septum, forces mouth breathing and can worsen nighttime respiratory issues. Smoking irritates and inflames the airways, increasing the likelihood of breathing disruptions. Understanding these contributing factors is the first step toward addressing the root causes of poor sleep quality.
How Breathing Disruptions Affect Sleep Quality Improvement
When breathing becomes compromised during sleep, the brain briefly rouses the body to restore normal airflow. These micro-awakenings, often unnoticed by the sleeper, prevent the deep, restorative sleep stages necessary for physical and mental recovery. Over time, this pattern leads to chronic sleep deprivation, even if you spend adequate hours in bed.
The consequences extend beyond tiredness. Poor sleep quality affects memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and cognitive function. Individuals may experience difficulty concentrating, irritability, mood swings, and reduced productivity. Physical health also suffers, with increased risks of high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. Recognizing the connection between breathing patterns and sleep quality is crucial for taking proactive measures to improve rest and overall health.
Recognizing Signs of Sleep-Related Breathing Problems
Common indicators of nighttime breathing issues include loud, persistent snoring, gasping or choking sounds during sleep, and witnessed pauses in breathing. Morning symptoms often include waking with a dry mouth or sore throat, headaches, and feeling unrefreshed despite adequate time in bed. Daytime symptoms encompass excessive sleepiness, difficulty staying awake during routine activities, poor concentration, and memory problems.
Partners or family members often notice these symptoms before the affected individual does. Keeping a sleep diary or using smartphone apps to record sleep sounds can provide valuable information for healthcare providers. If you experience these symptoms regularly, seeking professional evaluation is important for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Sleep Comfort Tips for Better Breathing
Implementing practical strategies can significantly improve nighttime breathing and sleep quality. Sleeping on your side rather than your back helps keep airways open by preventing the tongue and soft tissues from collapsing backward. Elevating the head of your bed by four to six inches can reduce airway obstruction and minimize acid reflux, which can worsen breathing problems.
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the airway and decreases the severity of breathing disruptions. Avoiding alcohol and sedatives for several hours before bedtime prevents excessive muscle relaxation in the throat. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep quality.
Keeping nasal passages clear through saline rinses, humidifiers, or allergy management can facilitate easier breathing. For those with chronic congestion, addressing underlying sinus issues or allergies with appropriate treatment can make a substantial difference. Creating a comfortable sleep environment with proper temperature, darkness, and minimal noise also contributes to uninterrupted rest.
Treatment Approaches and Professional Solutions
For individuals with persistent breathing disruptions, various treatment options are available. Continuous positive airway pressure devices deliver steady air pressure through a mask to keep airways open throughout the night. Oral appliances, fitted by dentists specializing in sleep medicine, reposition the jaw and tongue to maintain airway patency.
Surgical interventions may be considered for specific anatomical issues, such as removing enlarged tonsils or correcting a deviated septum. Positional therapy devices help train individuals to sleep in positions that minimize airway obstruction. Lifestyle modifications, including weight loss programs and smoking cessation, often form the foundation of comprehensive treatment plans.
Working with sleep specialists ensures accurate diagnosis through sleep studies and personalized treatment recommendations. Many treatment options are covered by insurance when medically necessary, though coverage varies by plan and provider.
Long-Term Health Implications
Left unaddressed, chronic breathing disruptions during sleep can lead to serious health complications. The repeated drops in blood oxygen levels strain the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of hypertension, irregular heartbeat, heart attack, and stroke. Metabolic problems, including insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, are more common among those with untreated sleep-related breathing disorders.
Mental health can also deteriorate, with higher rates of depression and anxiety observed in individuals experiencing chronic sleep disruption. The cumulative effects of poor sleep quality diminish overall quality of life and can shorten lifespan. Early intervention and appropriate treatment significantly reduce these risks and improve long-term health outcomes.
Understanding how breathing patterns affect sleep is essential for maintaining good health. By recognizing symptoms, implementing practical sleep comfort strategies, and seeking professional evaluation when needed, you can take meaningful steps toward achieving restorative sleep and protecting your long-term well-being.